OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organization of 14 oil-exporting developing nations that coordinates and unifies the petroleum policies of its Member Countries.
OPEC’s formation by five oil-producing developing countries in Baghdad in September 1960 occurred at a time of transition in the international economic and political landscape, with extensive decolonisation and the birth of many new independent states in the developing world.
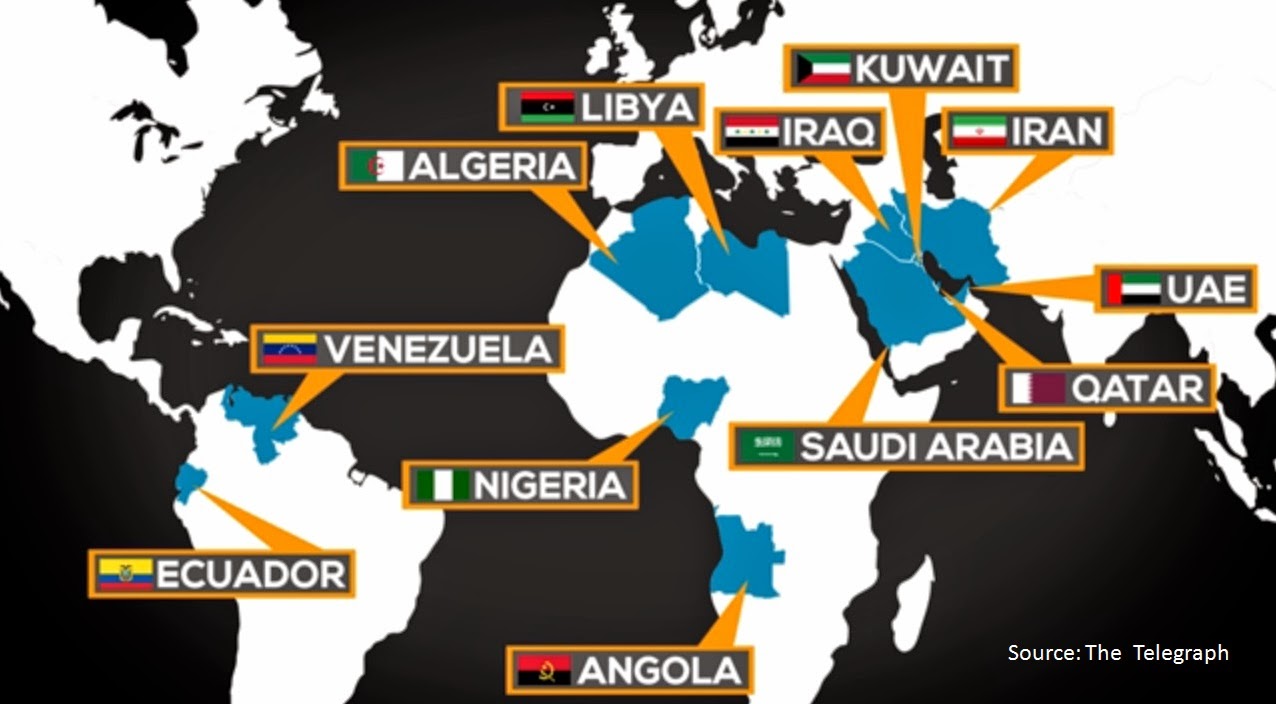
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was founded in Baghdad, Iraq, with the signing of an agreement in September 1960 by five countries and Founder Members of the Organization:
- Islamic Republic of Iran
- Iraq
- Kuwait
- Saudi Arabia
- Venezuela.
These countries were later joined:
- Qatar (1961)
- Indonesia (1962)
- Libya (1962)
- The United Arab Emirates (1967)
- Algeria (1969)
- Nigeria (1971)
- Ecuador (1973)
- Gabon (1975)
- Angola (2007)
From December 1992 until October 2007, Ecuador suspended its membership. Indonesia suspended its membership in January 2009, but this was reactivated in January 2016. Gabon terminated its membership in January 1995. However, it rejoined the Organization in July 2016.